Day 44-45 : Relational Database Service in AWS & Deploy Wordpress website on AWS
Amazon Relational Database Service (Amazon RDS) is a collection of managed services that makes it simple to set up, operate, and scale databases in the cloud
Task-01
1.Create an EC2 instance
Go to the Amazon EC2 console.
Click "Launch Instance".
Choose a Ubuntu AMI.
Choose an instance type, such as t2.micro.
Choose a VPC and subnet.
Configure security group rules to allow inbound traffic on the appropriate port for the type of database you are using (e.g. port 3306 for MySQL).

Launch the instance.

2.Create a Free tier RDS instance of MySQL
Go to the Amazon RDS console. Click "Create database".

Select "MySQL" as the engine type.

Choose the "Free tier" template for "DB instance class".

Enter a unique name for the "DB instance identifier".
Set the "Master username" and "Master password" for the database.

Set the "Virtual Private Cloud (VPC)" and "Subnet group" to create the instance in.
Leave the other settings at their default values.


Select ec2-instance

Choose VPC security group

Click "Create database" to start the instance creation.

Database is created.

3.Create an IAM role with RDS access.
Go to the IAM console. Click "Roles". Click "Create role".

Choose the 'AWS service'.
Choose "Allows EC2 instances to call AWS services on your behalf".

Attach the "AmazonRDSFullAccess" policy.

Enter a unique name for the role.

Click "Create role".
Role is created

4. Assign the role to EC2 so that your EC2 Instance can connect with RDS
Go to the EC2 console.
Select the instance you just created.
Click "Actions", then "Instance Settings", then "Attach/Replace IAM Role".

Choose the IAM role you just created.
Click "Update IAM role".

5.Once the RDS instance is up and running, get the credentials and connect your EC2 instance using a MySQL client.
Go to the RDS console.
Select the instance you just created.
Click "Configuration" and note the endpoint address.

Click "Security" and note the username and password.

SSH into your EC2 instance using a terminal or remote access tool.

Install a MySQL client, such as "mysql".

6.Connect to the RDS instance using the MySQL client and the endpoint address, username, and password:
mysql -h <endpoint address> -P <port.no> -u <username> -p
Enter the password when prompted and press enter.
You should now be connected to the MySQL database on the RDS instance.

7.create a database user for your WordPress application and give the user permission to access the wordpress database.
Run the following commands in your terminal:
CREATE DATABASE wordpress;
CREATE USER 'wordpress' IDENTIFIED BY 'wordpress-pass';
GRANT ALL PRIVILEGES ON wordpress.* TO wordpress;
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
Exit
- An Amazon RDS for MySQL database to store your WordPress data.


- Setup the server and post your new Wordpress app.To run WordPress, you need to run a web server on your EC2 instance.To install Apache on your EC2 instance, run the following command in your terminal:
sudo apt-get install apache2

Verify Apache web server is working on browsing public-ip of your ec2 instance.

Setup the server and post your new Wordpress app.
First, download and uncompressed the software by running the following commands in your terminal:
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gz
tar -xzf latest.tar.gz

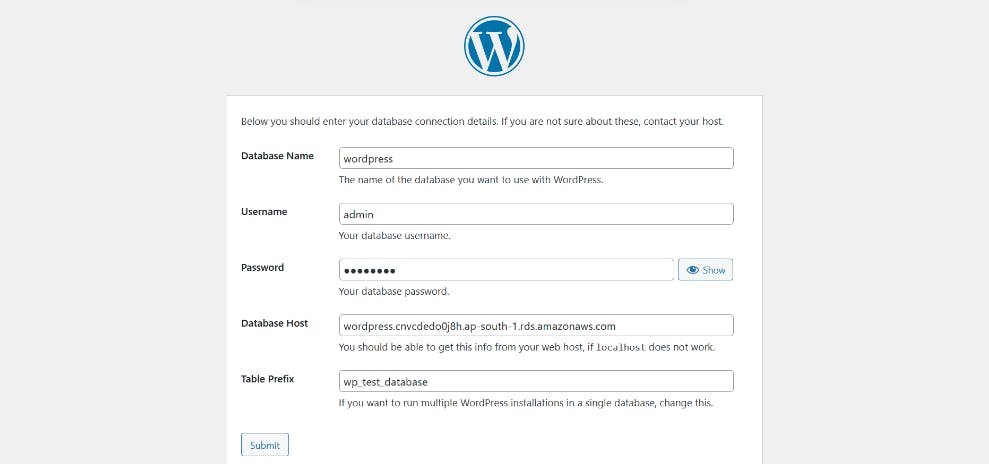
Change the directory to the wordpress directory and create a copy of the default config file using the following commands open the wp-config.php file

Edit the database configuration by changing the following lines:

DB_NAME: your RDS database name
DB_USER: The name of the user you created in the database in the previous steps
DB_PASSWORD: The password for the user you created in the previous steps
DB_HOST: The hostname of the database means your database endpoint from rds
The second configuration section you need to configure is the Authentication Unique Keys and Salts.
You can replace the entire content in that section with the below content:
define('AUTH_KEY', '@VZ<pXEL?vb-kiz(Zfp_R9f9|.+T-O/P$Z9|T-q%~|KX@,/(RZk00K{ybHA=6nT6')
define('SECURE_AUTH_KEY', '12Ip[Ts<IA>Vc+R#_X>i85OjMMRtks-o^E2(,$P[Q=f~Zt:@FrW1r$,` vqs|%@|');
define('LOGGED_IN_KEY', 'o*_:obJ!+wtc8&]QhK}-xEVv+eVD!hFbBzkxKn@}(gK{-{d|l-?9b)8+)tfx8zjl');
define('NONCE_KEY', 'Ue<fX0Z71vg7Y&F+~CqM-G%N~ozMe%?qrp-@|tTVh??zJ4:~Sm,VhTKBE0C7DY(?');
define('AUTH_SALT', 'v.Z^1,QR66F-CDW=t<daxxk-;|M3cC{XzF`rn#l[U]f-fboHZYY/c8nvYU(uM`a]');
define('SECURE_AUTH_SALT', 'Cz$[Mq>)Hc=BSo,&Q%;,r}Eu7!:>nj4N91WeIx|7jp=fc+S64lMXCNj|h&a9Q5[D');
define('LOGGED_IN_SALT', 'Y{[of`B<!<<Za+|YtiMJkd33@a}+I%-0u}EPmAx?hW~$_(( u iuIJ2UQUJIv7(Q');
define('NONCE_SALT', 'g<!-Nhqy2E{X{87!|x{Amg3v:Z%e8d(z3l9x|g-T uB62u4xuw?uyjS_>1Yl]~Kw');;
Install the application dependencies you need for WordPress. In your terminal, run the following command.
sudo apt install php libapache2-mod-php php-mysql -y

Copy your WordPress application files into the /var/www/html directory used by Apache.
sudo cp -r wordpress/* /var/www/html/

restart the Apache web server
systemctl restart apache2
Browse "ec2-public-ip/wp-admin/" you should see the WordPress welcome page.
Thank you for reading!
