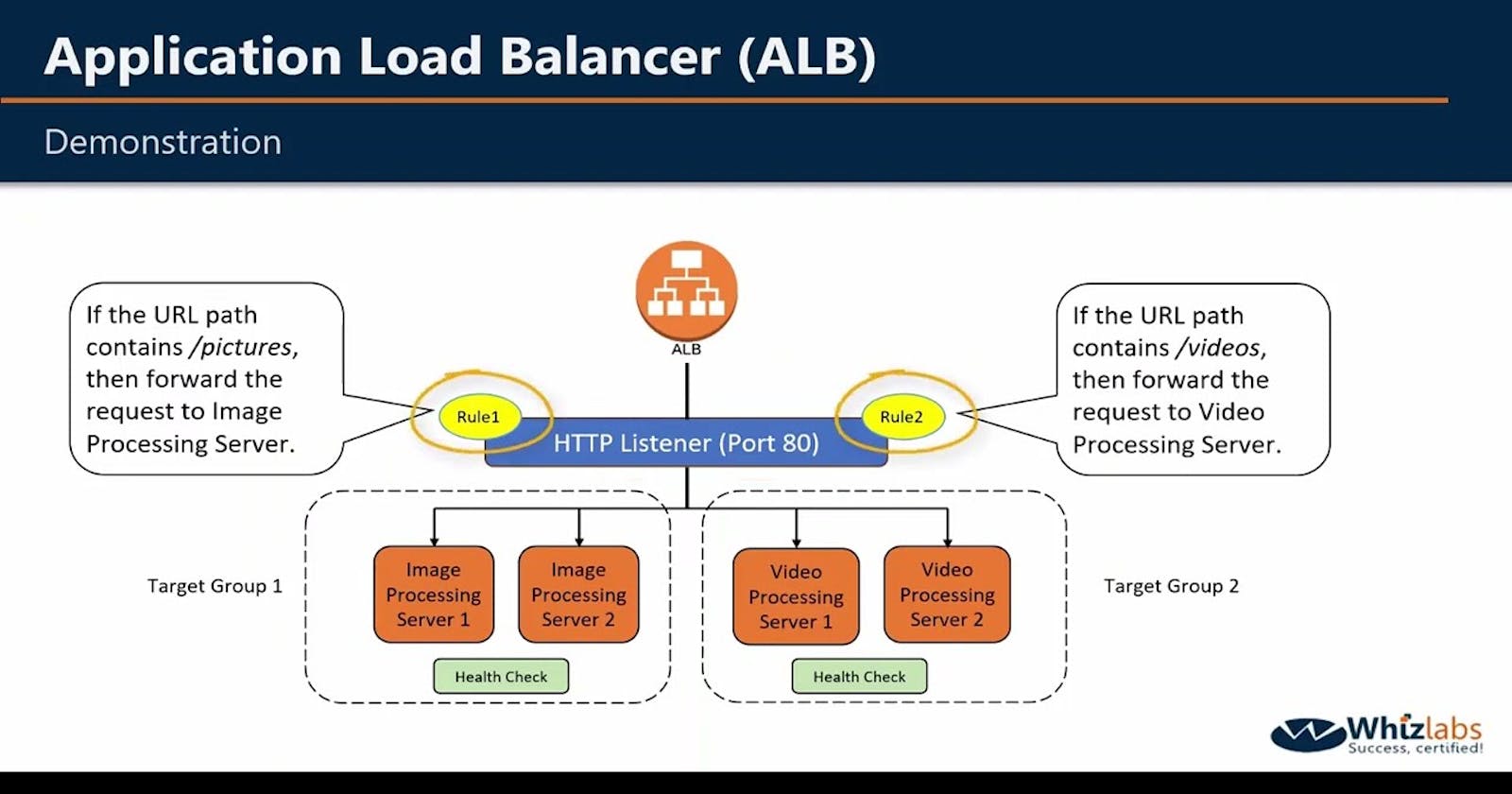
What is Load Balancing?
Load balancing is the distribution of workloads across multiple servers to ensure consistent and optimal resource utilization. It is an essential aspect of any large-scale and scalable computing system, as it helps you to improve the reliability and performance of your applications.
Elastic Load Balancing:
Elastic Load Balancing (ELB) is a service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that automatically distributes incoming traffic across multiple EC2 instances. ELB provides three types of load balancers:
Application Load Balancer (ALB) - operates at layer 7 of the OSI model and is ideal for applications that require advanced routing and microservices.
Network Load Balancer (NLB) - operates at layer 4 of the OSI model and is ideal for applications that require high throughput and low latency.
Classic Load Balancer (CLB) - operates at layer 4 of the OSI model and is ideal for applications that require basic load balancing features.
Today's Tasks:
Task 1:
launch 2 EC2 instances with an Ubuntu AMI and use User Data to install the Apache Web Server.
Log in to your AWS Console and go to the EC2 dashboard.
Click on the "Launch Instance" button and select "Ubuntu Server ".

Choose the instance type, configure the instance details, add storage, and configure security groups as required.
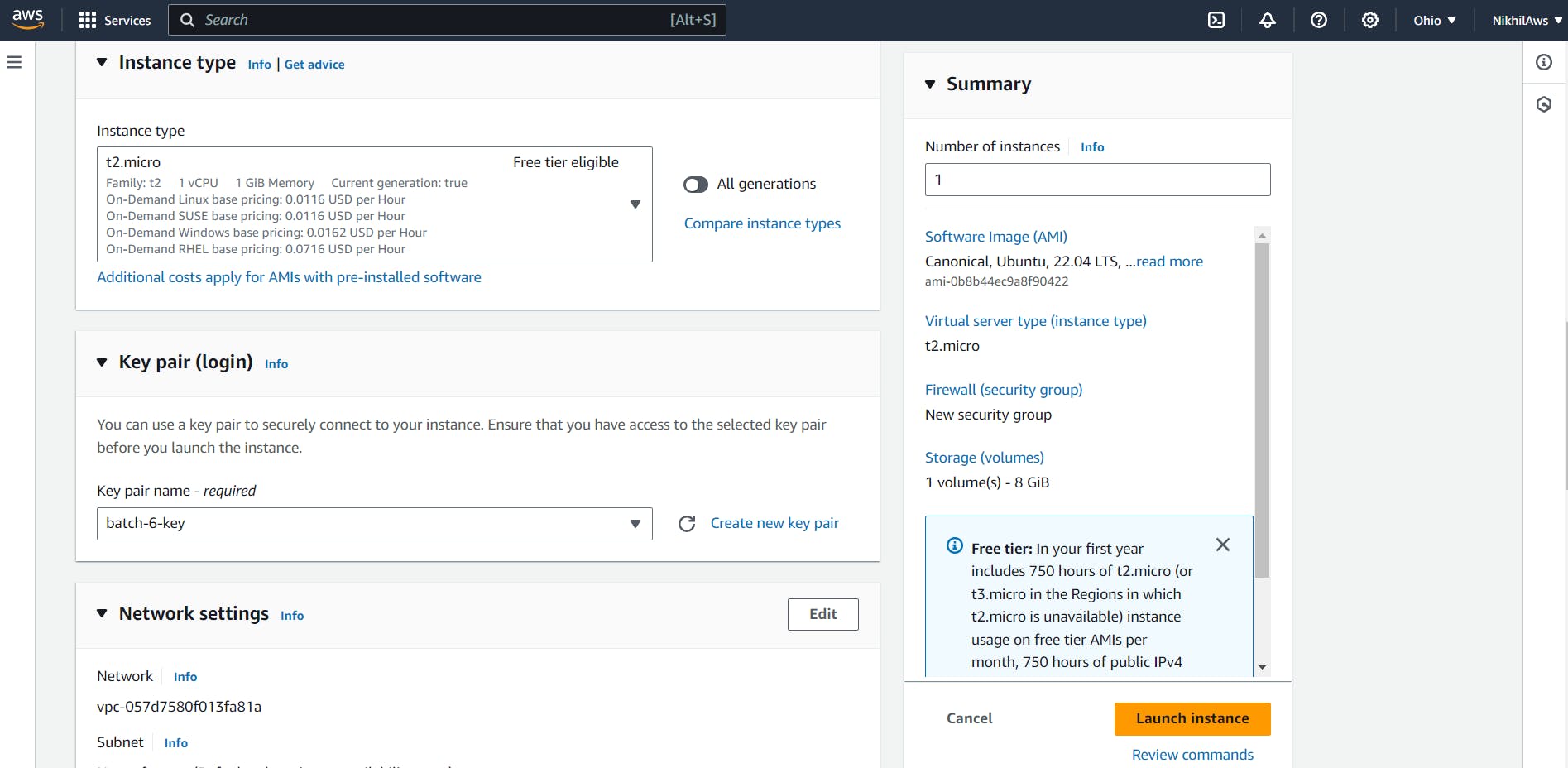
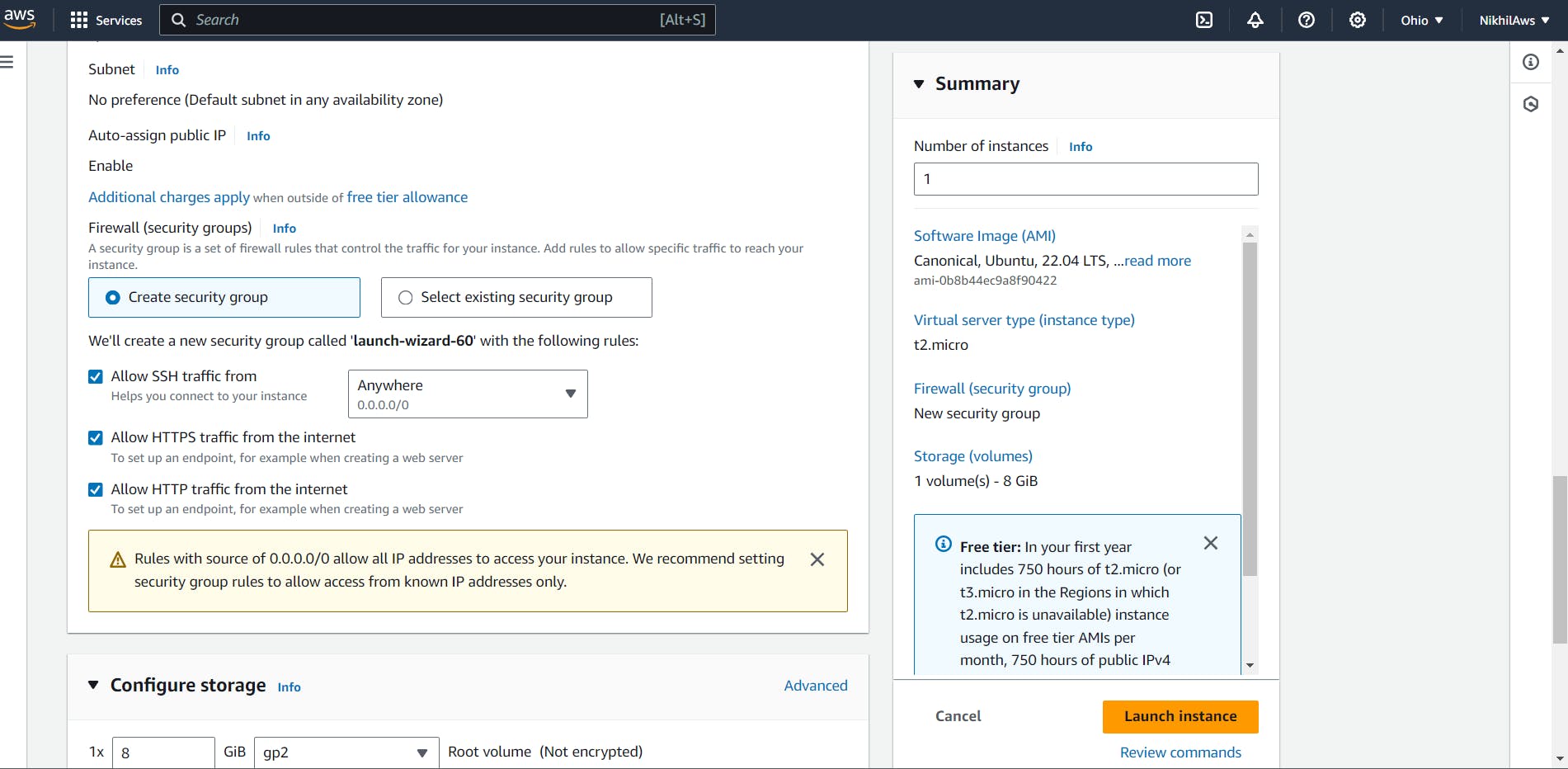
In the "Configure Instance Details" page, scroll down to the "Advanced Details" section and expand the "User data" field.
In the "User data" field, enter the following commands to install and start the Apache web server:

You can see two instances are created.

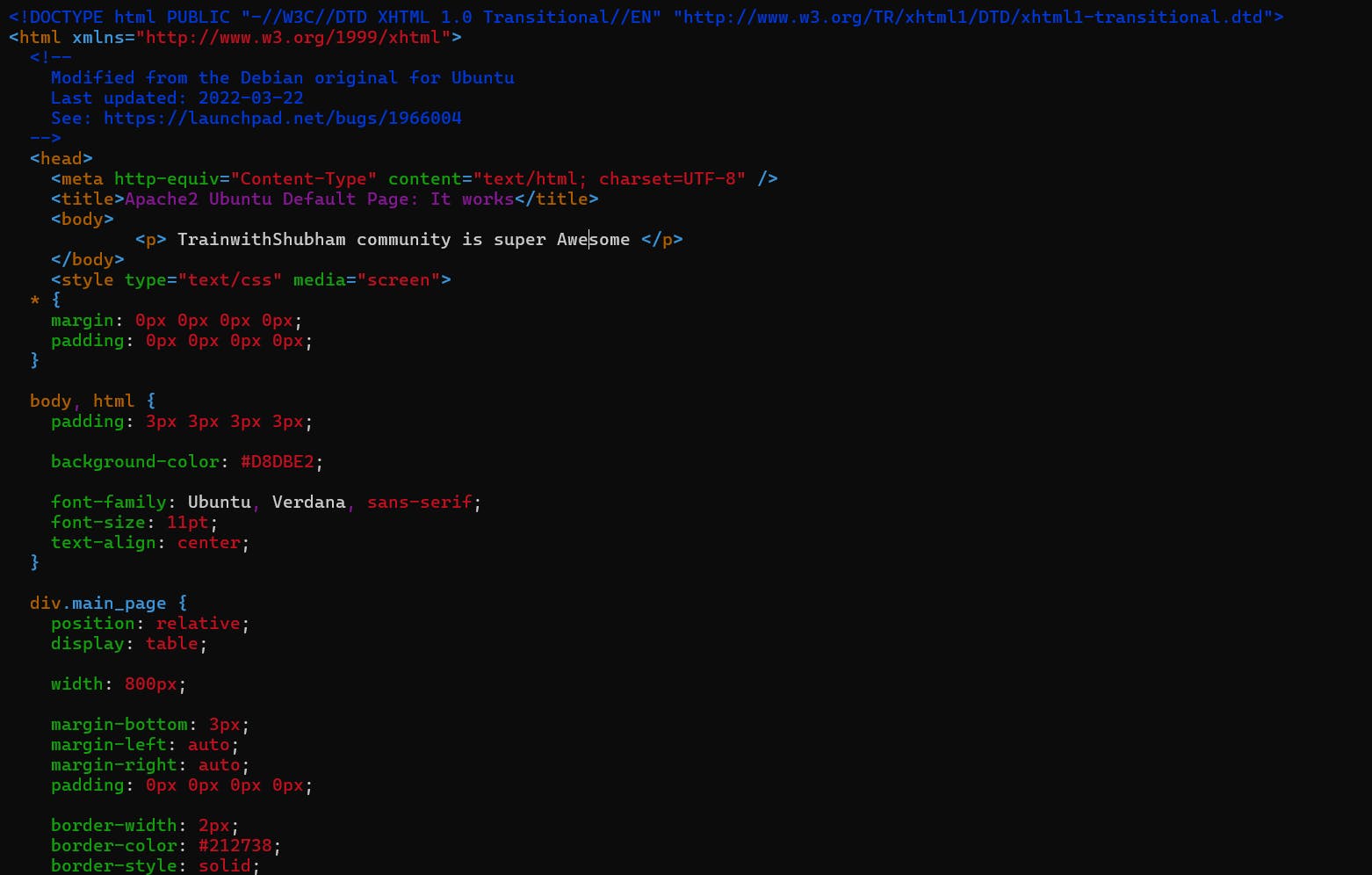
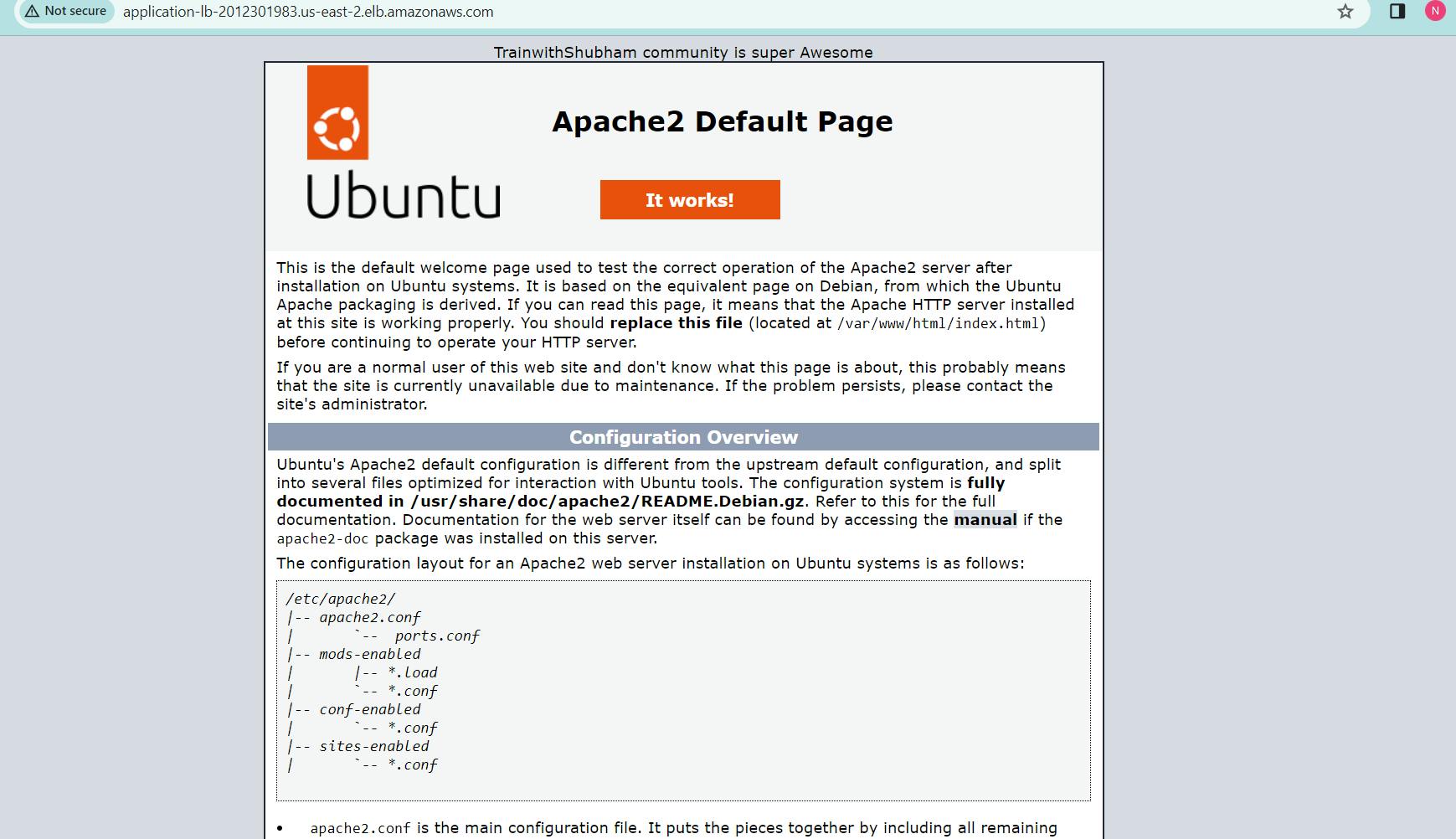
Modify the index.html file to include your name so that when your Apache server is hosted, it will display your name also do it for 2nd instance which include " TrainWithShubham Community is Super Awesome :) ".
For apache-server1
Check apache2 status using below command:

Go inside /var/www/html path and edit index.html file
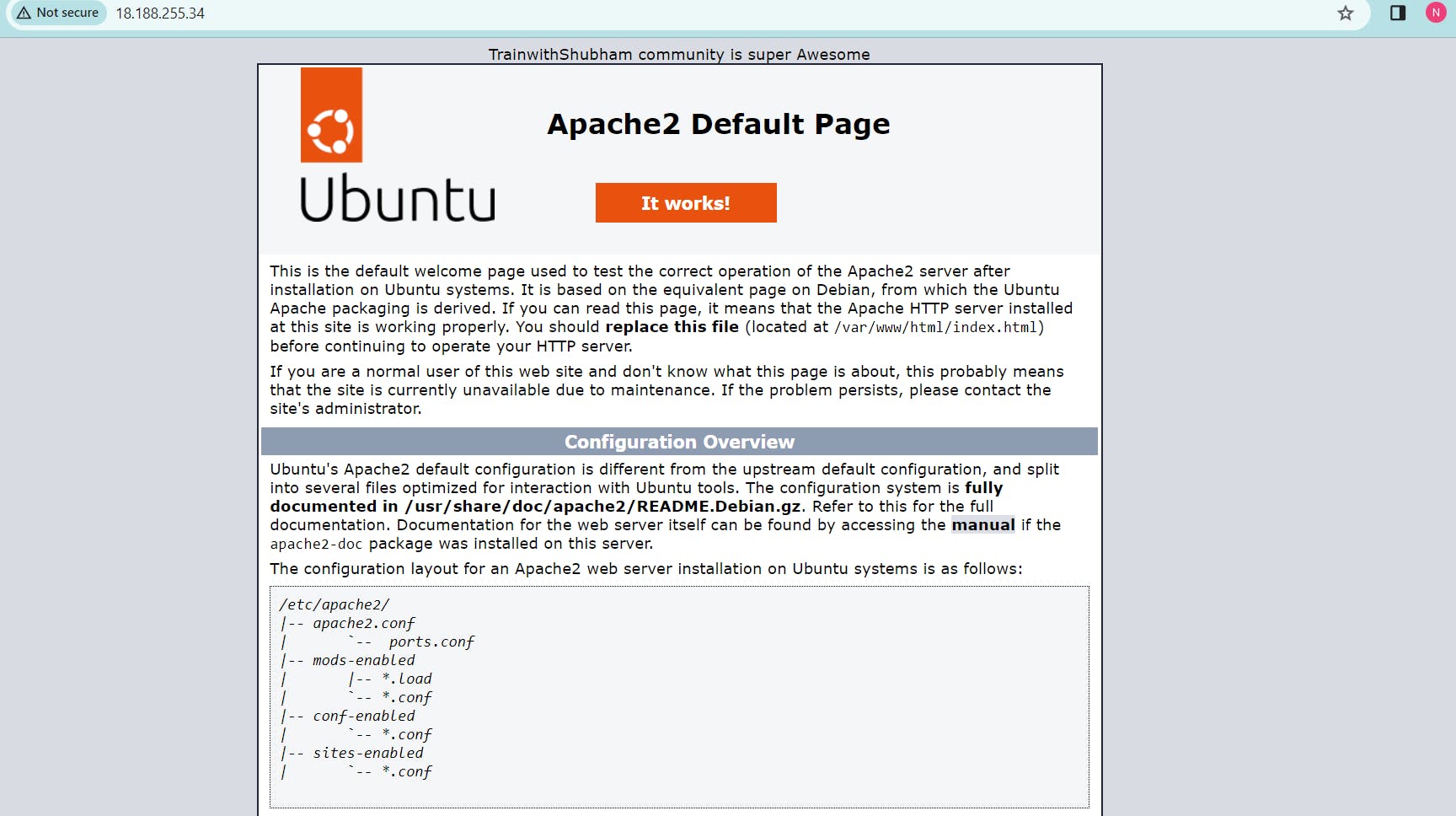
Copy the public IP address of your EC2 instances.
Open a web browser and paste the public IP address into the address bar.
You should see a webpage displaying information about your PHP installation.

For apache-server2:
Check apache2 status.
Go inside /var/www/html path and edit index.html file
Copy the public IP address of your EC2 instances.
Open a web browser and paste the public IP address into the address bar.
You should see a webpage displaying information about your PHP installation.
Task 2:
Create an Application Load Balancer (ALB) in EC2 using the AWS Management Console.
Log in to the AWS Management Console and go to the EC2 dashboard.
Click on "Load Balancers" in the left-hand navigation menu and then click the "Create Load Balancer" button.

Select "Application Load Balancer" as the load balancer type and click "Create".

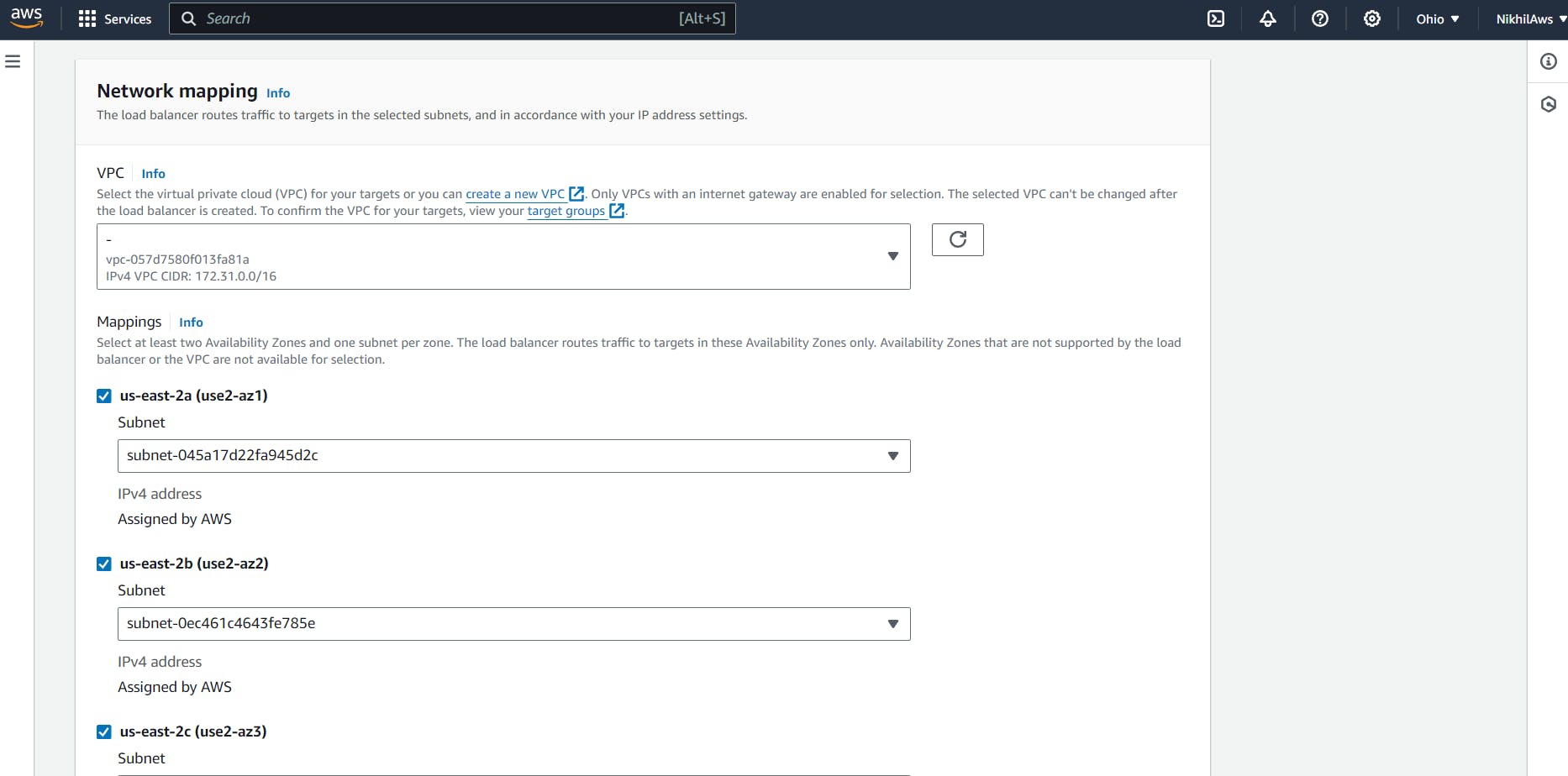
Configure the load balancer settings, such as name, listener, security group, and availability zones. For the listener, you can choose HTTP or HTTPS, depending on your application's requirements.

Configure "Security Groups"

Create a target group by specifying a name, protocol, port, and health check settings. Choose the same availability zones as the load balancer and select the instances that you launched in Task 1 as targets for the target group.
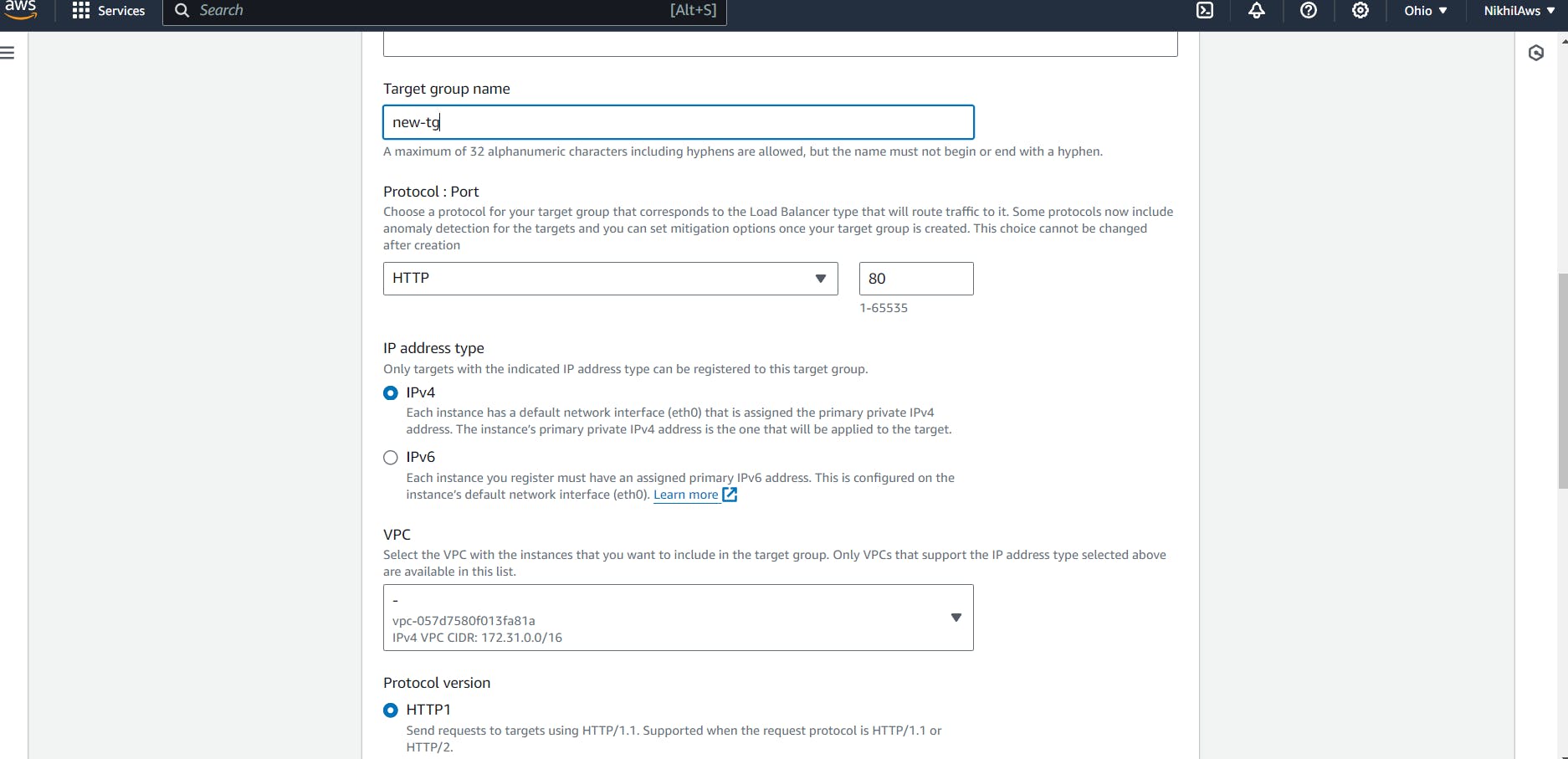
Add EC2 instances which you launch in task-1 to the ALB as target groups.

Load balancer is created.

Target group is created.
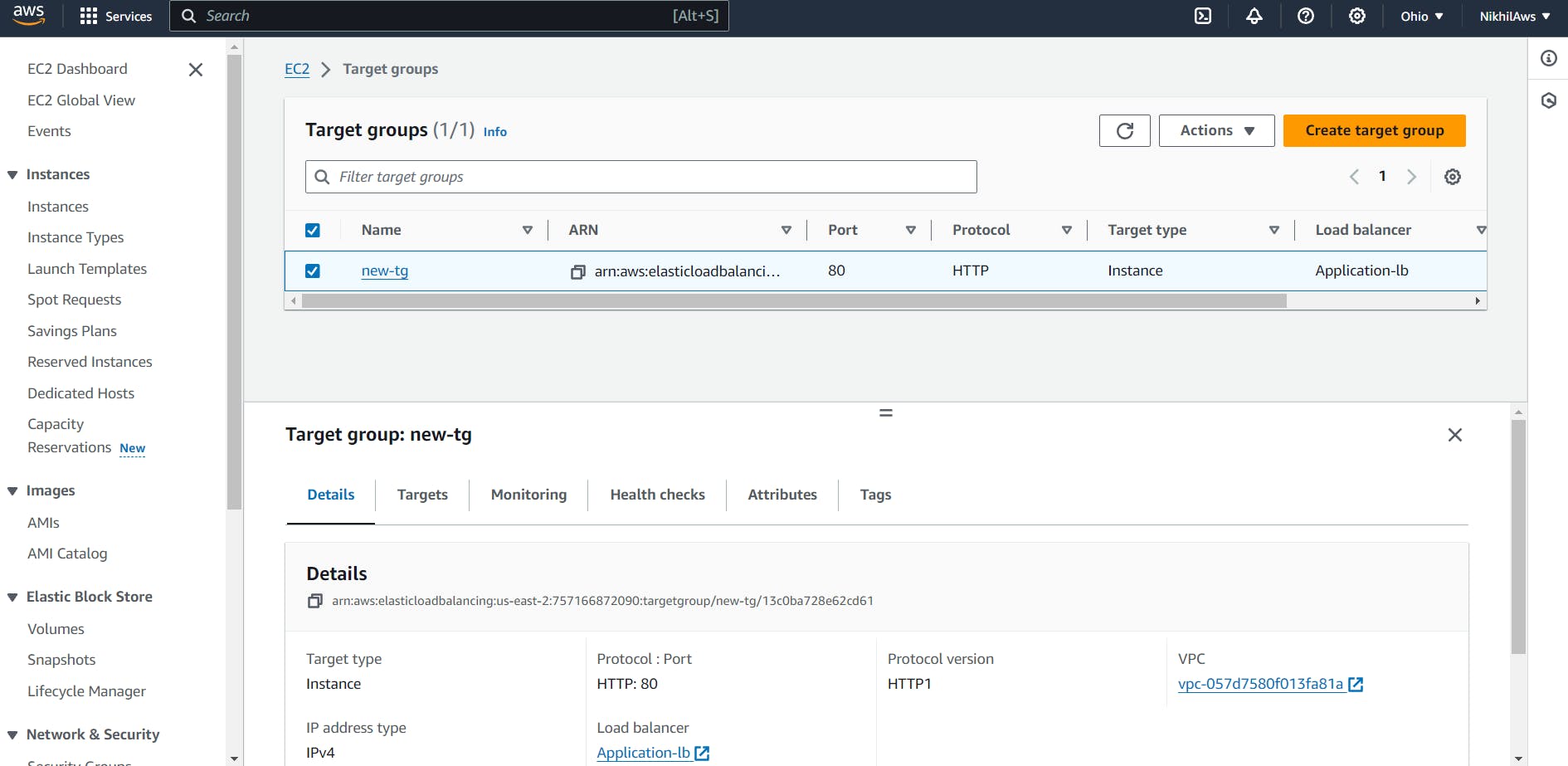
Verify that the ALB is working properly by checking the health status of the target instances and testing the load balancing capabilities.
Verify that the instances are registered with the load balancer by checking the target group's health status. You should see a healthy status for all instances in the group.

Test the load balancing capabilities by accessing the load balancer's DNS name in a web browser . You should see traffic being evenly distributed across the instances.

Thank you for reading!